-p-500.jpg)
Explore our detailed guide and free downloadable template for a Disturbed Thought Process Nursing Care Plan, including diagnosis, interventions, and nursing software solutions. Perfect for healthcare professionals.
-p-500.jpg)
By Telita Montales on Jul 18, 2024.
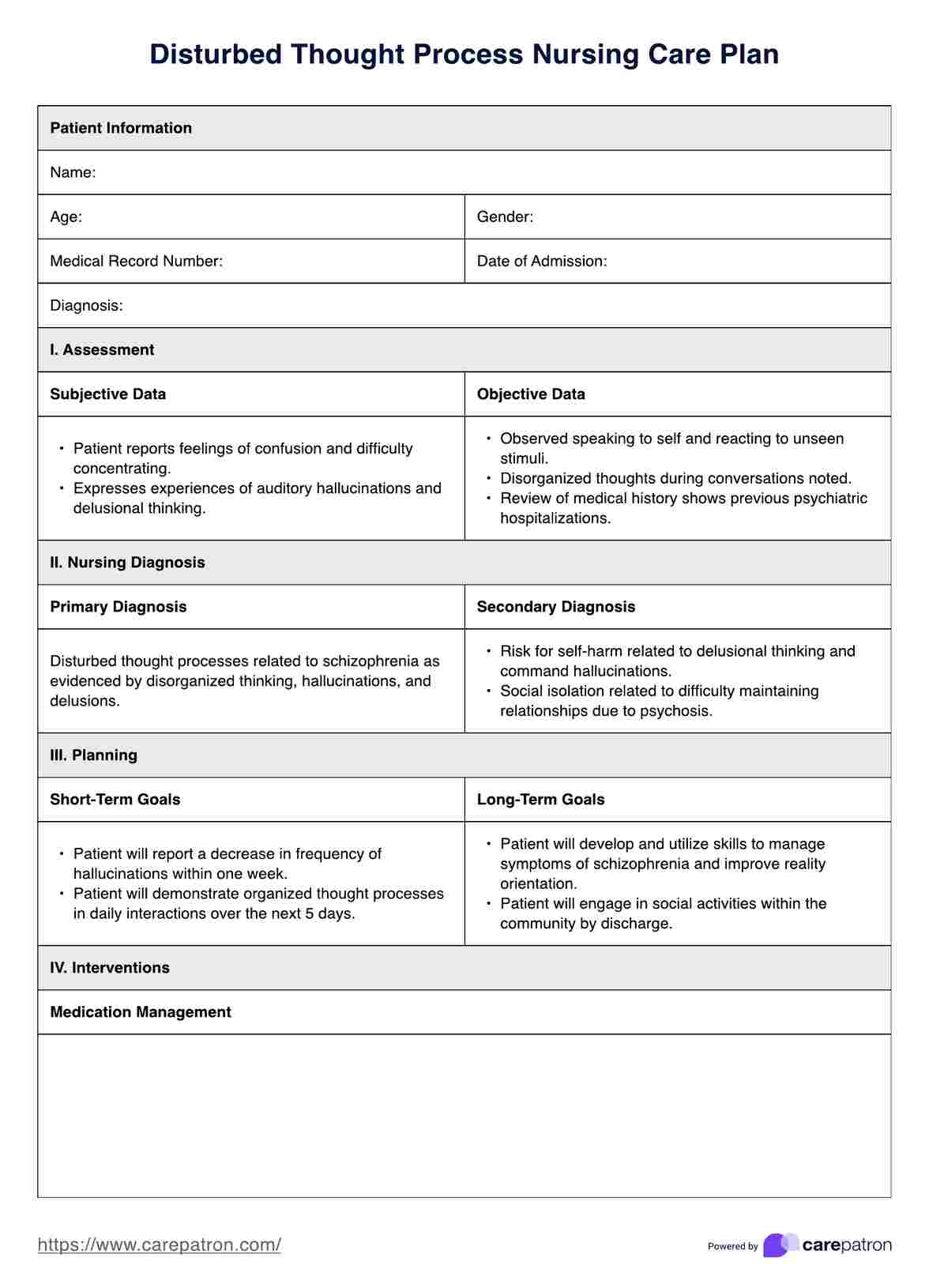

A disturbed thought process, often recognized in patients with mental health disorders, refers to a disruption in cognitive operations and activities. This condition can manifest as disorganized thinking, impaired decision-making, difficulty concentrating, and irrational beliefs. Common in conditions like schizophrenia, dementia, and severe depression, it significantly impacts a person's ability to function daily.
The causes of disturbed thought processes are diverse, typically involving a combination of genetic, biochemical, and environmental factors.
Neurological diseases like Alzheimer's can directly impair cognitive functions, while mental health disorders such as schizophrenia may disrupt thought patterns due to biochemical imbalances. External stressors, drug abuse and traumatic experiences also play a crucial role in exacerbating this condition.
PDF Template Example PDF
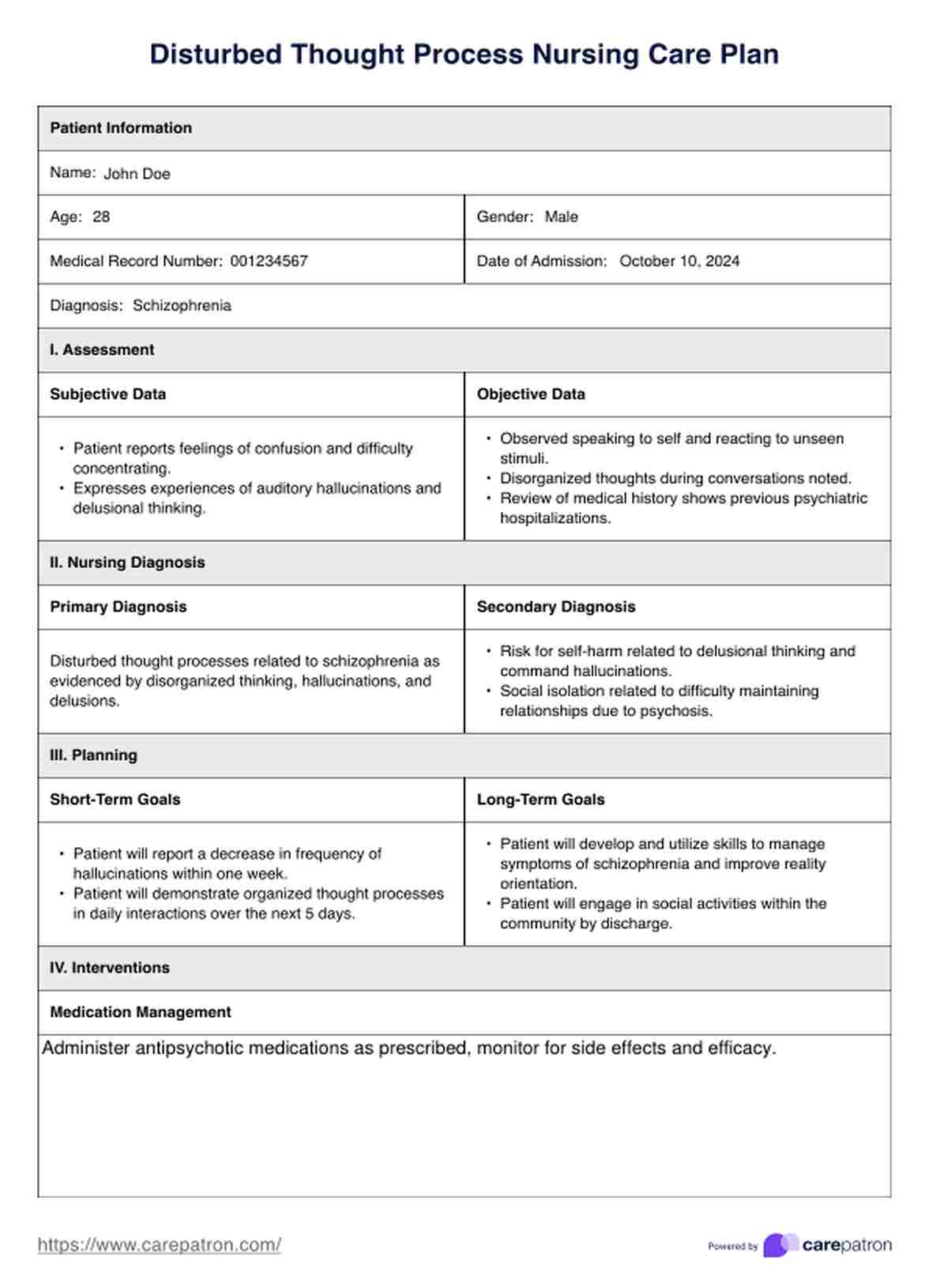
Here's how nurses assess and diagnose illogical thinking and disturbed thought processes:
Nurses start by observing the patient’s behavior for signs of disorganized thinking, illogical thought patterns, anxiety, and difficulty making decisions. Listening to family members' concerns about the patient’s recent behaviors and social interactions also provides crucial insights for nursing diagnoses.
A thorough review of the patient’s medical and psychiatric history helps identify factors present and the underlying conditions contributing to cognitive disturbances.
Structured cognitive tests and psychological assessments evaluate and assess the severity and specific characteristics of the thought disturbances.
Laboratory tests may be conducted to rule out or confirm any biochemical imbalances or medical conditions that might be affecting the patient's cognitive functions.
Nurses collaborate with psychiatrists or neurologists to develop an appropriate treatment plan based on the assessment. Continuous monitoring and adjustments ensure the interventions remain effective as the patient's condition evolves.
Our printable Disturbed Thought Process Nursing Care Plan provides a structured approach to developing a comprehensive care plan for patients with disturbed thought processes. It includes sections documenting patient history, symptoms, assessment findings, and planned interventions.
Nurses can customize the template to reflect specific patient needs, ensuring all relevant factors are considered and addressed. This tool is essential for maintaining thorough documentation and effective patient care.
Interventions for disturbed thought processes typically focus on the following:
These interventions collectively provide safety measures and support managing disturbed thought processes tailored to the patient's needs to maximize their independence and improve their quality of life.
Our free Disturbed Thought Process Nursing Care Plan is an essential tool in the management of patients with cognitive impairment or a disturbed thought process, offering numerous benefits that enhance both patient care and healthcare delivery:
A well-drafted care plan ensures that every aspect of care is tailored to meet the patient's unique needs. This personalized approach considers the individual’s specific mental health challenges, lifestyle, and social context, making interventions more likely to be effective and accepted by the patient. Consistency in care is crucial for patients with mild cognitive impairment, as it helps minimize confusion and reinforce a stable environment.
Targeted interventions, as outlined in a care plan, directly contribute to better patient outcomes. By addressing the root causes and symptoms of disturbed thought processes, these tailored strategies help reduce episodes of disorientation, enhance cognitive function, and prevent the progression of symptoms. This strategic approach helps stabilize mental disorders over time, contributing to an overall improved quality of daily life for the patient.
A comprehensive care plan is a central reference for all team members involved in a patient’s care, from nurses and physicians to specialists and support staff.
This document provides a clear overview of the patient’s condition, goals, and planned interventions, ensuring every team member has the information they need to provide consistent care.
Enhanced communication through nursing care plans leads to better coordination among caregivers, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring that the patient receives the most effective treatment possible.
With a complete care plan, decisions regarding changes in treatment or necessary interventions can be made quickly and with greater confidence.
The care plan provides a documented basis for these decisions, particularly important in complex cases involving multiple health professionals. This can be critical in emergencies or when the patient’s condition changes rapidly.
Comprehensive care plans also play a vital role in involving patients and their families in the care process. By understanding the care plan, families can better support the patient at home, helping to manage symptoms and implement non-medical interventions that can improve outcomes.
Open communication facilitated by a clear care plan helps families understand the patient’s condition, reducing anxiety and building trust between healthcare providers and the patient’s support network.
Regular reviews of the care plan allow for ongoing monitoring of the patient’s progress and the effectiveness of the implemented strategies.
This ensures that the care provided remains appropriate as the patient’s needs evolve and allows for the timely adjustment of strategies to address any emerging issues or changes in the patient’s condition.
A comprehensive care plan is more than just a document; it is a dynamic tool that enhances the care process, supports healthcare providers, involves families, and, most importantly, centers on the patient’s needs, promoting better health outcomes and a higher quality of life.